by Igor | Jun 23, 2015 | Linux, Odoo, Programming
It is possible to work on the local computer (workstation) with Ubuntu, local virtual machine or in a server over the network.
I prefer to do the development work in my personal workstation, using my favorite text editor or IDE.
So this is my development setup:
VirtualBox + Ubuntu + PyCharm
VirtualBox works on Linux, Windows and OS X so i can move VM’s from one platform to another.
The assumption is that you have installed Ubuntu desktop.
You can download and install Ubuntu from this location:
http://www.ubuntu.com/download/desktop/thank-you/?version=14.04.2&architecture=amd64
You can download and install VirtualBox from this location:
https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
The Ubuntu installation process has already guided you in the creation of a user.
You will use that user to setup you development environment.
First, make sure you are logged in as the user created during the installation process, and not as root.
Assuming your user is netjunky:), you can confirm your home directory and user with the following commands:
echo $HOME
whoami
Now we can install Odoo directly from the GitHub repository and install our favorite IDE.
1.) Install system updates
sudo apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y
2.) Install Git
sudo apt-get install git -y
3.) Install PostgreSQL Server
sudo apt-get install postgresql -y
4.) Install Python dependencies
sudo apt-get install python-dateutil python-feedparser python-ldap python-libxslt1 python-lxml python-mako python-openid python-psycopg2 python-pybabel python-pychart python-pydot python-pyparsing python-reportlab python-simplejson python-tz python-vatnumber python-vobject python-webdav python-werkzeug python-xlwt python-yaml python-zsi python-docutils python-psutil python-mock python-unittest2 python-jinja2 python-pypdf python-decorator python-requests python-passlib python-pil python-pip -y
5.) Create a directory to work in. This will create work directory for your projects ~/projects/odoo-dev
mkdir ~/projects
mkdir ~/projects/odoo-dev
6.) Go into our work directory
cd ~/projects/odoo-dev
7.) Get Odoo source code from gitub (-b option asks to explicitly download the 8.0 branch of Odoo)
git clone https://github.com/odoo/odoo.git -b 8.0
8.) Install Odoo system dependencies. Just one more check with odoo.py script. I did not bother to investigate but if you try to run this command before step 4. you will get errors about missing python dependencies.
./odoo/odoo.py setup_pg
9.) Create PostgreSQL superuser
./odoo/odoo.py setup_pg
10.) Install wkhtml and place on correct place for Odoo
sudo wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/wkhtmltopdf/archive/0.12.1/wkhtmltox-0.12.1_linux-trusty-amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i wkhtmltox-0.12.1_linux-trusty-amd64.deb
sudo cp /usr/local/bin/wkhtmltopdf /usr/bin
sudo cp /usr/local/bin/wkhtmltoimage /usr/bin
sudo rm -rf wkhtmltox-0.12.1_linux-trusty-amd64.deb
To start an Odoo server instance, just run odoo.py:
~/projects/odoo-dev/odoo/odoo.py
Odoo server is ready and we can now install PyCharm or some other favorite text editor or IDE.
To install PyCharm community edition:
sudo wget -q -O - http://archive.getdeb.net/getdeb-archive.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://archive.getdeb.net/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc)-getdeb apps" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/getdeb.list'
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install pycharm -y
Run PyCharm
cd /usr/share/pycharm/bin
./pycharm.sh
Or you can skip all the steps and run this script:)
https://gist.github.com/netjunky-hub/ac65b479fc4a306ae6bc
Make sure you are not using root (don’t use sudo to run the script).
WARNING!
Script will download and configure Odoo, remove Libre office and install Apache Open Office, install useful tools like meld, pgadmin3 and poedit, download and install Odoo templates for PyCharm, create directories for custom config and custom addons.
You can adjust script to fits your needs.
Happy coding:)
by Igor | Jun 5, 2015 | Linux
How to create your own squid proxy server on CentOS
Squid is a proxy server for caching and filtering web content .
Squid proxy service will cache the requested web-content and re-using it for the further request of the same content.
You can also hide your real IP with squid and access content usually forbidden for your country or IP address.
Requirement is that you have already installed your CentOS server.
1.) Connect with putty to install and configure squid
yum update
yum install squid
cd /etc/squid3
Make backup of default configuration just in case…
cp squid.conf squid.conf.bak
Remove default configuration
rm -rf squid.conf
Create and open new configuration in nano (you can use any other editor)
nano squid.conf
Paste this 2 lines of code into your new configuration file
http_access allow all
http_port 20000
Save configuration
6.) Start squid service
service squid start
7.) To check your connection use telnet IP on port defined in your squid configuration.
In this case 20000
telnet IP 20000
Your proxy server is ready if your connection was successiful.
Setup your OS to use this proxy server and go to http://whatsmyip.org to check your new IP address.
Don’t forget to open port 20000 on your server firewall.
Check this article to configure squid on Ubuntu:
http://netjunky.net/how-to-create-your-own-squid-proxy-server-with-azure/
by Igor | Jun 4, 2015 | Linux
How to create your own squid proxy server with Azure and Ubuntu OS.
Squid is a proxy server for caching and filtering web content .
Squid proxy service will cache the requested web-content and re-using it for the further request of the same content.You can also hide your real IP with squid and access content usually forbidden for your country or IP address.
1.) Sign in to your Azure Portal and create VM

2.) Choose Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS
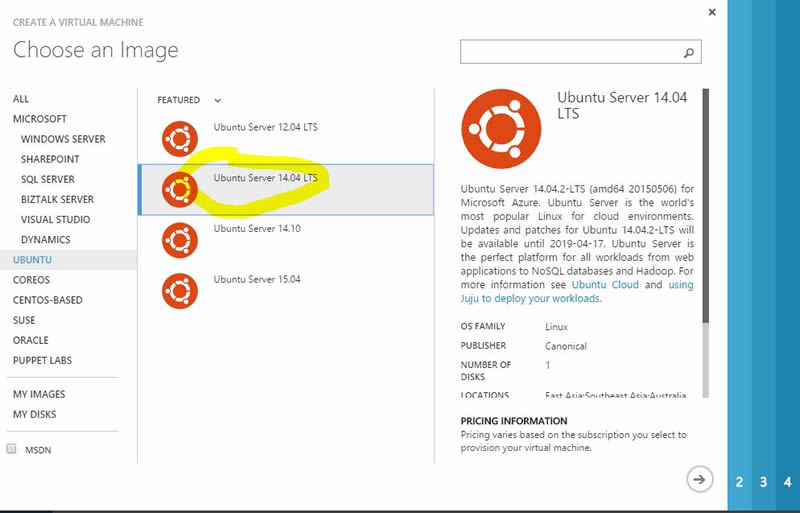
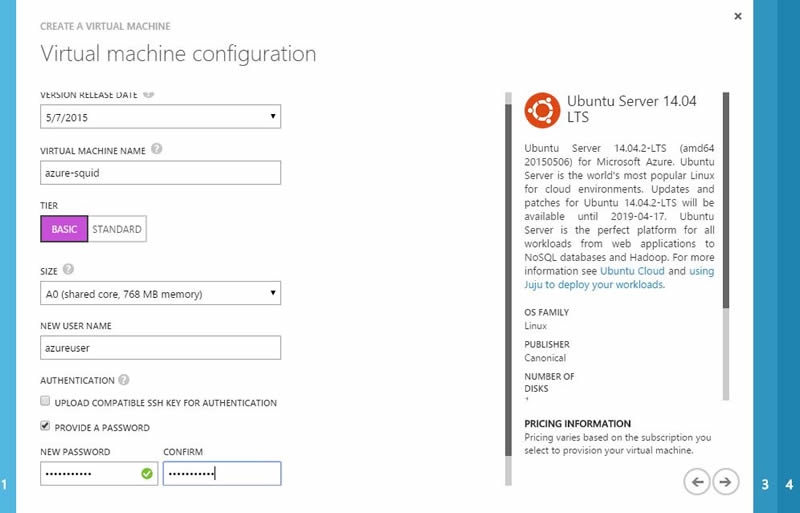
3.) Configure your VM
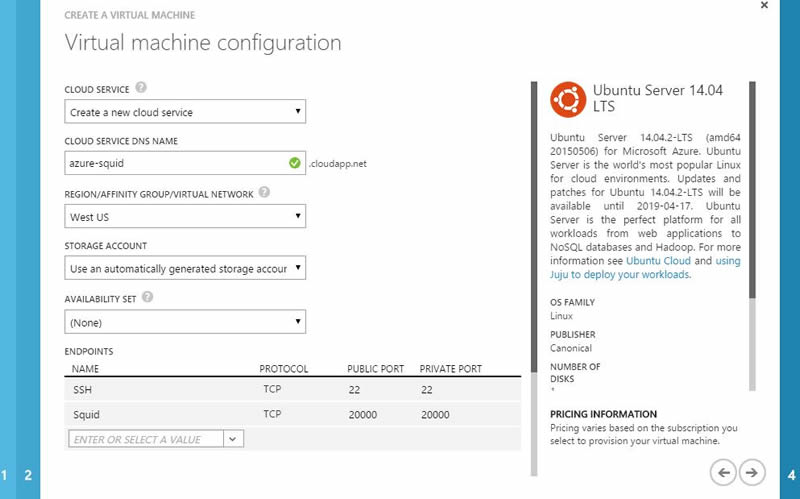
4.) Create endpoint higher then 1024 for example 20000
5.) Connect with putty to install and configure squid
sudo apt-get install squid -y
cd /etc/squid3
Make backup of default configuration just in case…
sudo cp squid.conf squid.conf.bak
Remove default configuration
sudo rm -rf squid.conf
Create and open new configuration in nano (you can use any other editor)
sudo nano squid.conf
Paste this 2 lines of code into your new configuration file
http_access allow all
http_port 20000
Save configuration
6.) Restart squid service
sudo service squid3 restart
7.) To check your connection use telnet IP on port defined in your squid configuration.
In this case 20000
telnet IP 20000
Your proxy server is ready if your connection was successiful.
Setup your OS to use this proxy server and go to http://whatsmyip.org to check your new IP address.
by Igor | May 28, 2015 | Linux
How to install Apache OpenOffice 4.1.1 on Ubuntu and Debian – 32 bit OS
First thing is to remove the already installed versions of either openoffice and libreoffice:
$ sudo apt-get remove libreoffice* openoffice*
$ sudo apt-get autoremove
Next, we will download openoffice, extract the archive and install the deb packages:
$ wget sourceforge.net/projects/openofficeorg.mirror/files/4.1.1/binaries/en-US/Apache_OpenOffice_4.1.1_Linux_x86_install-deb_en-US.tar.gz
$ tar -xzvf Apache_OpenOffice_4.1.1_Linux_x86_install-deb_en-US.tar.gz
$ cd en-US/DEBS
$ sudo dpkg -i *.deb
$ cd desktop-integration
$ sudo dpkg -i *.deb
How to install Apache OpenOffice 4.1.1 on Ubuntu and Debian – 64 bit OS
First thing is to remove the already installed versions of either openoffice and libreoffice:
$ sudo apt-get remove libreoffice* openoffice*
$ sudo apt-get autoremove
Next, we will download openoffice, extract the archive and install the deb packages:
$ wget sourceforge.net/projects/openofficeorg.mirror/files/4.1.1/binaries/en-US/Apache_OpenOffice_4.1.1_Linux_x86-64_install-deb_en-US.tar.gz
$ tar -xzvf Apache_OpenOffice_4.1.1_Linux_x86-64_install-deb_en-US.tar.gz
$ cd en-US/DEBS
$ sudo dpkg -i *.deb
$ cd desktop-integration
$ sudo dpkg -i *.deb
Optional to remove Apache OpenOffice 4.1.1 on either 32 bit or 64 bit Ubuntu and Debian, do
$ sudo apt-get remove openoffice*
To start OpenOffice 4.1.1 from terminal use
$ openoffice4

That’s it!
by Igor | May 27, 2015 | Linux, Odoo
Sometimes you may encounter an error in development or production [Errno 98] Address already in use.
This error is due to openerp-service or some other service already use port defined in your Odoo config.
You could try to change the port 8069 to any other port and restart the server but that’s not the right way.
Just apply the command
sudo ps aux | grep openerp
which will show you the port on which openerp server is in running state.
Then kill the specific process.
sudo kill -9 id
For example sudo kill -9 999
Restart odoo server and that’s it.
by Igor | May 26, 2015 | Linux
By default sudo remembers your password for 15 minutes.
Disable sudo timeout with this command:
sudo sh -c 'echo "\nDefaults timestamp_timeout=-1">>/etc/sudoers'
To re-enable sudo timeout use this command:
sudo sed -i "/Defaults timestamp_timeout=-1/d" /etc/sudoers
You can also change or disable sudo timeout with visudo.
sudo visudo
This opens an editor and points it to the sudoers file — Ubuntu defaults to nano, other systems use Vi.
To the defaults line, add :
timestamp_timeout=2
So it will look like this:
Defaults env_reset,timestamp_timeout=20
You might want to read the sudoers manual pages for additional information.
man sudoers






Recent Comments